Appsavio Coding Standards
- Naming Conventions
- Comments
- Coding style
- SOQL Rules
- Trigger Standards
- Apex Batch Standards
- Apex Test Class Standards
- Flow Standards
- VS Code Must Have Extensions
Naming Conventions
-
Use US-English for naming identifiers.
-
Use Pascal and Camel casing for naming identifiers. In Pascal casing, the first letter of each word in an identifier is capitalized. For example, UserStory. In Camel casing, only the first letter of the second, third, etc. word in a name is capitalized. for example, userStory.
| IDENTIFIER | CASE | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Class | Pascal | Account |
| Enum type | Pascal | Severity |
| Enum values | Pascal | Severity.Error |
| Field | camel | listItem |
| Final/Const field | Pascal | MaximumCount |
| Static field | Pascal | RedValue |
| Interface | Pascal | Idisposable |
| Method in Apex, Java | camel | toString |
| Method in C# | Pascal | ToString |
| Parameter | camel | typeName |
| Property | Pascal | BackColor |
| Trigger | Pascal | SendEmailOnNewAccount |
In Apex, primitive types such as String, Decimal are all classes. So they should be Pascal casing.
-
Do not use Hungarian notation or add any other type of identification to identifiers.
Hungarian notation means to put the variable type prior to its name. For example: strName, intAge. -
Do not use an underscore in identifiers.
Avoid using underscore “_” in identifiers. It is deprecated in most companies.
Exception In Apex, underscores exist in the name of every custom field and custom object as “__c” or “__r”, and in a managed package. When you create a custom field/object, Remove the blank spaces in the name to avoid unnecessary underscores. In other words, blank spaces could appear in the label, but not in the name. -
Name an identifier according to its meaning and not its type. Every Identifier should be meaningful.
-
Use a noun or a noun phrase to name a class, field, or property.
Classes, fields, and properties should be noun phrases.
The name for a Visualforce page can either be a noun or verb phrase. -
Use a verb or a verbal phrase to name a method or trigger.
Methods and Triggers do actions, so they should be verbal phrases. -
Suffix exception classes with Exception. Classes derived from Exception are special. They should have the suffix Exception. For example, DmlException, AcceptLeadException, EsclateCaseException.
-
Suffix controller classes with Controller For example, AssignCaseToDealerController
-
Suffix test classes with Test, test class name will be Class Name + Test, For example, we have a controller named AssignCaseToDealerController, the test class name is AssignCaseToDealerControllerTest
-
Use a plural noun to name a collection, For example,
Set<Id> accountIds = new Set<Id>();
Comments
- Each class/trigger shall contain a header block.
The description should include useful information about what it is, why you created it, and any known issues or dependencies:
/**
* @description : Description of the class
* @author : Author Name
* @created Date : CreatedDate
* @last modified on : LastModifiedDate
* @Test class: Name of Test class for this class
**/
You can download the VScode extension named Salesforce Documenter
-
Use // for single line comments.
Use // instead of /* */ if the comments is a single line. -
Comments shall be written in US English
-
Verbs in comments shall be of singular form in the third person.
- Write necessary comments, not redundant or noisy.
For example, everybody knows that is a default constructor:
public class Whatever{ //default constructor Public Whatever(){ } } -
Separate class members and code sections with a blank line. Remove unnecessary blank lines. Blank lines are treated equally as comments. Use them to separate class members. For example, each method should be separated by a blank line.
If a method contains more than one operation, separate them with blank lines. Do remove unnecessary blank lines in your code. -
Remove the commented lines from production.
For some reason, we need to comment some lines out when coding Please remember to remove them before deploying them to production. - No need to comment if the code can explain itself.
Coding style
- Put the opening brace “{“ to a new line.
Java developers used to put the opening brace in the same line of the block definition, like:
public class Whatever{ //not recommended }
This is not about right or wrong, but we make an agreement to put it to the next line, like:
public class Whatever
{
//recommended
}
This rule applies to all kinds of code blocks, including class, method, property, if-else, while, etc.
- Use blank spaces properly
Use blank spaces properly as betrayed in the following table:
| EXPRESSION | BLACK SPACE | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetical operator | 1 | b + c |
| Assignment | 1 | a = b + c |
| Comparison | 1 | a >= b + c |
| Semi-colon | 0 | a = b + c; |
| if/while | 1 | if (a == b + c) |
| for loop | 1 | for (i = 0; i < 100; i++) |
| Unary operator | 0 | <p>!bool </p><p>-i</p> |
| Increment/Decrement | 0 | <p>i++ </p><p>–i</p> |
| Ternary operator | 1 | (a == null) ? 0 : a |
| Function call | 0 | sendEmail(email); |
| Subscript | 0 | array[0] |
| Automatic property | 1 | <p>String Name { get; </p><p>set; }</p> |
Example:
a = b + c; // right
a=b+c; // wrong
a = b + c ; // wrong
a = (a == null) ? 0 : a; // right
a = (a == null)?0:a; // wrong
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) // right
for(i=0;i<10;i++) // wrong
for (i = 0; i < 10; i ++) // wrong
a = -- b; // wrong
a = --c; // right
a = - b; // wrong
a = -b; // right
public String Name{get;set;} // wrong
public String Name { get; set; } // right
-
SOQL and SOSL should be readable on the screen without much scrolling so make sure to separate lines in SOQL to make it more readable in a single glance.
-
All flow control primitives (if, else, while, for, do, switch) shall be followed by a block, even if it is empty.
Example:
If () {}
- A Tab space should be of four spaces no more no less. Change your IDE settings to set the Tab spaces to Four.
SOQL Rules
- The SOQL keywords should be in UPPERCASE for example.
[SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Website = 'Test'] //Recommended
[select Id, Name From Account where Website = 'Test']
//Not Recommended
-
It is recommended to have a single query on an Object in a Single piece of code. The developer should get the records to be used at once and store them in containers accordingly.
-
The Query should contain a valid Where clause condition to minimize the records returned from the query. The more records Query returns the more time Apex transaction will take. Also, there’s a limit of 50000 records returned per Query. So it’s better to filter data as much as possible in the Query itself.
-
It is not recommended to store the Query resulted records in a list directly if there can be lots of records. It will impact the heap size and may terminate the transaction. A better way would be to use Query as the Value parameter of the forEach loop.
//Not Recommend
List<Account> acctList = [SELECT Id FROM Account];
for( Account acct : acctList ){
//Process here
}
//Recommend
for( Account acct : [SELECT Id FROM Account] ){
//Process here
}
-
Avoid querying fields that are of no use for your logic. It will increase the Transaction time and Heap memory with unnecessary data.
-
Utilize child queries instead of Querying child records in another Query.
//Not Recommend
List<Account> acctList = [ SELECT Id, Name FROM Account ];
List<Opportunity> oppList = [ SELECT Id, Name
FROM Opportunity
WHERE Account Id IN: acctList];
//Recommend
List<Account> acctList = [ SELECT Id, Name
( SELECT Id FROM Opportunities )
FROM Account ];
- Maintain the spaces
//Recommend
[ SELECT Id, Name FROM Account Where Id IN: keySet() ];
//Not Recommend
[SELECT Id,Name FROM Account Where Id IN:keyset()];
Enterprise Structure
To keep the code sophisticated and easy to maintained developers should write their code in a well-mannered structure that will keep the different parts of the at their appropriate places.
The General structure for coding is below:
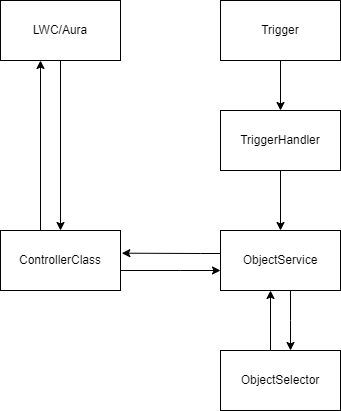
Trigger
The Apex Trigger should contain only the Trigger session logics ( After, Before, Insert Update ). It should not contain any business-related logic. Based on different sessions the trigger should call the methods or the TriggerHandler class.
trigger TriggerAccount on Account{
if( Trigger.isBefore ){
if( Trigger.isInsert ){
AccountTriggerHandler.setAccountAge( Trigger.Name );
}
}
if( Trigger.isAfter ){
if( Trigger.isInsert ){
AccountTriggerHandler.createAccountContacts( Trigger.Name );
}
}
}
TriggerHandler
To handle the Data to be inserted or modified developers should create a TriggerHandler class. TriggerHandler should have separate methods for each functionality and should be called from Trigger inappropriate conditions. TriggerHandlers should call the methods from the Object Specific Service Class method that contains all the business logic. It is not recommended to have any DML in TriggerHandler class. An example of TriggerHandler is as follows:
public class AccountTriggerHandler{
public static void setAccountAge( List<Account> newAccounts ){
List<Account> acctList = new List<Account>();
for( Account acct : newAccounts ){
if( acct.Email != null ){
acctList.add( acct );
}
}
AccountService.setAccountAge( acctList );
}
public static void createAccountContacts( List<Account> newAccounts ){
AccountService.createAccountContacts( newAccounts );
}
}
ObjectService class
The Object Service class contains all the business logic for the object. This class is named after the sObject name. For example, AccountService will contain all the logic for happening on the Account object same for other standard and custom objects. This makes it easy to find and resolve the issues and also keeps the code clean and structured. An example of a Service class is given below:
public class AccountService{
public static void setAccountAge( List<Account> newAccounts ){
//Business logics here
}
public static void createAccountContacts( List<Account> newAccounts ){
//Business logics here
}
}
ObjectSelector class
The selector classes contain all the queries for the specific objects. For example, the AccountSelector class will contain all the SOQL happening on the Account object in this org. Then this method should be called from different classes. This class layer helps to detect the Governer limits spend and resolve them. It helps developers to monitor easily which queries they are using and also helps in Code reusability. An example for Selector class is as follows.
public class AccountSelector{
//Following method can be called from Service or Controller class.
public static List<Account> getAccountsById( Set<Id> accIds ){
return [ SELECT Id, Name, Website FROM Account WHERE Id IN: accIds ];
}
}
Controller class
Controller classes are created specifically for Lightning Components and Vifsualforce pages. These classes contain the component-specific logic but as far as business-related logic is considered controller classes call the methods from the Service classes to perform DML on records. It is not recommended to have DMLs in Controller classes. Following is an example for the Controller class structure.
public class AccountPageController{
@AuraEnabled
public static List<Account> getAccountDetails( Set<Id> accIds ){
return AccountSelector.getAccountsById( accIds );
}
@AuraEnabled
public static void updateAccounts( List<Account> acctList ){
AccountService.updateAccounts( acctList );
}
}
Trigger Standards
-
If the purpose of trigger is to Update fields of the Same object on which Trigger is written, always write code in Before Trigger context.
-
If a related Object is to be inserted or modified, write your code in After Trigger context.
-
Keep the one Trigger per Object. Create a Trigger Handler class that further processes the business logic.
-
Keep Trigger clean. Keep as less logic as possible inside the Trigger file and move all logic into TriggerHandler and Service classes.
-
Triggers must be Bulkified. Every method called from your trigger should expect multiple records to be processed. This will ensure Trigger functionality when bulk loading of data.
-
Trigger Name should follow Naming conventions like:
‘Trigger’+ObjectName
For Example TriggerOpportunity or TriggerAccount
- The trigger should have separate If sections for each session. For example
if( Trigger.isBefore ){
if( Trigger.isInsert ){
//Call all Before Insert Methods here
}
if( Trigger.isUpdate ){
//Call all Before Insert Methods here
}
if( Trigger.isDelete ){
//Call all Before Insert Methods here
}
}
if( Trigger.isAfter ){
if( Trigger.isInsert ){
//Call all After Insert Methods here
}
if( Trigger.isUpdate ){
//Call all After Insert Methods here
}
if( Trigger.isDelete ){
//Call all After Insert Methods here
}
}
-
For Projects with a bunch of Triggers it is recommended to utilize this Trigger Framework. This will keep the Trigger logic easier to implement and maintain.
-
It is recommended to have custom settings to disable and enable the Triggers manually or programmatically.
Apex Batch Standards
-
Get most of the reusable data in the Start method of your batch class instead of doing the same thing in Execute method.
-
It is recommended to return QueryLocator instead of queried records from the Start method as Query locator can get more records ( 50 million ).
-
Only implement interfaces like Database.Stateful or Database.Callout when they are actually required in code.
-
It is recommend to keep the batch class Public instead of Global.
-
Unless the batch processing time is too high, always try to run Batch with Batch Size 1.
-
It is recommended to log the total records processed/Failed inside the Batch Finish method.
Apex Test Class Standards
- Test classes Naming conventions should be like below examples:
- AccountTriggerHandlerTest
- AccountServiceTest
- AccountControllerTest
- LeadUpdateBatchTest
- Apex Test class should be Private and Without sharing.
@isTest
private class AccountServiceTest{
}
-
It is recommend to not use SeeAllData=True in test classes unless its the last option. Using this will make test classes run on bigger volume of data and also impact the data security.
-
The required Test Data should be inserted in the @TestSetup method and then should be quired in various test methods to pass in methods. Test setup method is called before every Test Method and provides a fresh data to process.
@isTest
private class AccountServiceTest{
@TestSetup
static void createData(){
Account acct = new Account( Name = 'Test Account' );
insert acct;
//Further records insertion below
}
}
- Test class should have different Method for each functionality. For example if you have two method in your AccountTriggerHandler, One updates the Account Website and another one creates a child opportunity then your Test Class should have two Test Methods one for each.
@isTest
static void accountWebsiteUpdateTest(){
//Logic to test Website test
}
@isTest
static void accountOpportunityInsertTest(){
//Logic to test Opportunity Insert
}
- Make sure you call the code to be tested inside the Test.startTest() and Test.stopTest(). This will make your test ignore the System limits and run your code in Test context.
@isTest
static void accountWebsiteUpdateTest(){
Account acct = [SELECT Id FROM Account LIMIT 1];
Test.startTest();
AccountService.accountWebsiteUpdate( acct );
Test.stopTest();
}
- Test class Test methods should contain System asserts to check if the functionality is working or not. Test class should not be created only for the coverage. It should contain proper validation of each functionality performing by the testing code. System asserts should always be after the Test.stopTest(), this will make sure your asserts run after all the asynchronous transactions are ended.
@isTest
static void accountWebsiteUpdateTest(){
Account acct = [ SELECT Id FROM Account LIMIT 1 ];
Test.startTest();
AccountService.accountWebsiteUpdate( acct );
Test.stopTest();
Account updatedAccount = [ SELECT Id, Website FROM Account WHERE Id =: acct.Id ];
System.assertEquals( 'myTestWebsite.com', updatedAccount.Website, 'Provide Error message here is assert fails' );
}
-
If your Testing code tests bulkified data then create atleast 200 records to test in Test Setup method.
-
It is recommended to create a separate TestDataFactory class that has code to create the records of various SObjects and call its methods inside your TestSetup or TestMethods.
-
It is recommended to have atleast 85% coverage of the main class.
-
Create logics in your test class to cover all If and Else blocks.
Flow Standards
-
Trigger Flow’s After and Before context should follow the same rules as Apex Trigger context.
-
If the Flow is Before then don’t use the DML Action on the same object instead use the Assignment Action and just assign values inside the Record variable.
-
It is recommended to keep the Flow easy to read and analyse.
-
If a Flow logic is common and can utilized in other flows then please create Separate flow with the Logic and use it as SubFlow inside your main Flow.
-
If Flow has lots of components then break the flow into different Small flows and use them in a Single flow as SubFlows. It will make the Flow easy to read and maintain.
- There should be only one Record Trigger flow for one Object for one Context. Naming conventions should be like below Account flow example:
- AccountBeforeFlow
- AccountAfterFlow
-
It is recommended to have a Success screen as last screen of a Screen flow.
-
It is recommended to have Description on every Action block used. It will work just like we do comments in code.
-
Don’t use Hardcoded Ids in the flow.
-
Flows has 2000 elements execution limit. For example if developer is looping over 1000 records and there are four Action elements used like Decision, Assignment, DML, loop element. Then total element execution limit will be 1000*4 = 4000 which will exceed the limit and throw error.
-
Make sure your formulas are not very complex. Formulas are calculated at runtime and can make your Flow run slow.
-
Proper error handling is must in all type of Flows. Use fault paths and show appropriate error messages.
- Screen flows have different context to run code( Enforcing Sharing, Without Enforcing Sharing, System Mode ). Make sure you are using appropriate context.
VS Code Must Have Extensions
APEX PMD
Apex PMD will provide useful tips about how you can optimize the code and make it better.
Salesforce Package XML generator
This extension will help to create Package.xml file with various Salesforce Metadata elements. It provides a rich UI that makes it convenient to create desired package xml files that can be used in Deployments.
Salesforce Query Editor
If you don’t like to Open developer whenever you want to query some records, you may like this extension. It will rich UI for Building your Query and show the returned records in a tabular format.
Beautify
Beautify provides code formatting natively for JS, HTML and CSS. Other than these languages it can be utilized for Apex and Visualforce as well. Apex can be formatted as per javascript standards. This extension doesn’t require any extra installation or configurations.
Snippets Extensions
These extensions will help you by providing auto completion for your code syntax. Following are some recommendations: